How to Get Baby in Head Down Position
- Why is the fetal position important?
- What are the different fetal positions during pregnancy?
- What are the risk factors for having a hard fetal position?
- Tin can the fetal position be corrected?
- How is belly mapping done?
- What are the other means to know the position of the infant?
Why Is The Fetal Position Important?
The fetal position tin can decide the ease or difficulty of your childbirth. Your babe may assume one of various possible babe birth positions past the stop of the gestation menstruation, which is likewise a deciding cistron for a vaginal nascency or cesarean commitment.
If your infant has shifted to a head-get-go position by the terminate of the term, they can descend through your vaginal opening without difficulty during delivery. However, if your baby doesn't motion to a feasible position, your OB/GYN may decide on an alternative commitment method.
This post discusses the various fetal positions your baby may present in when you're in labor and its bear upon on the delivery process.
Different Fetal Positions During Pregnancy
Before the due engagement, your babe volition drop down into the pelvis. Hither are the different positions your baby can go into when y'all are preparing for your delivery.
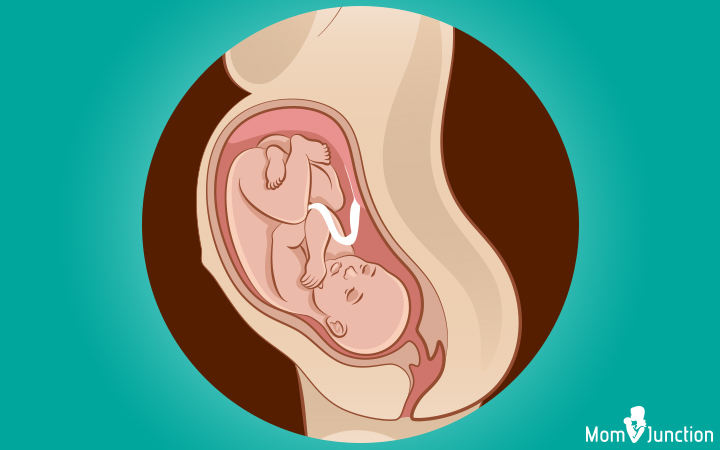
1. Occiput anterior (OA)
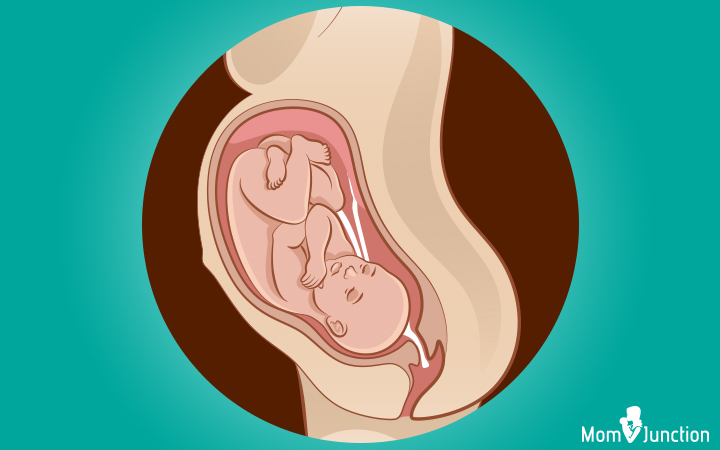
This is the ideal position your baby could accomplish towards commitment. The baby moves into the pelvis with her head-down, facing the female parent's back with chin tucked to the chest. Her caput points towards the birthing culvert. This is called the longitudinal lie.
Termed the vertex presentation of the fetus, this position is generally attained between 32nd and 36th weeks of gestation (1). The baby volition stay in the aforementioned position for the remainder of your pregnancy. This position is considered ideal for the baby to come out of the birthing canal with head first.
There are 2 more than presentations in the OA position:
i. Confront and brow presentation: (2) The baby volition remain in the OA position, merely her face and non head will be pointing towards the nascency canal. This happens when her chin is pointing outward instead of beingness tucked against the breast. The doctor can identify this position during a vaginal examination, by feeling the bony jaws and the mouth of the baby.
In brow presentation, the baby will be in the OA position just her forehead volition exist pointing towards the birth canal. During the vaginal test, the doctor can feel the anterior fontanelle and the orbits of the forehead.
ii. Chemical compound presentation: The infant is positioned anteriorly with i of her arms lying forth her head pointing towards the birthing culvert. The artillery may slide back during the delivering procedure, but when they don't, then extra care needs to be taken while taking out the baby safely.
[ Read: What Is Occiput Posterior? ]
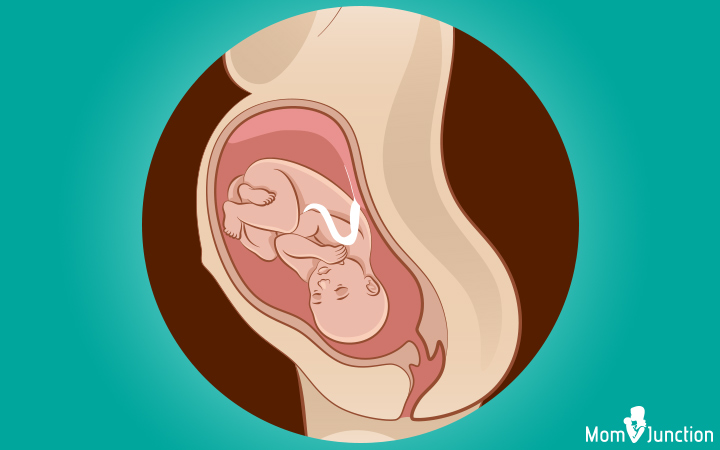
2. Occiput posterior (OP)
The baby moves into the pelvis with her head-down but facing the front/abdomen of the mother. This position is besides known as 'sunny-side up' or 'confront' position. OA and OP are called the cephalic or caput-get-go positions.
By and large, effectually 10-34% of babies remain in OP position during the starting time stage of labor and then turn to the optimal (OA) position. Merely, some remain in this position, which can make labor difficult, resulting in emergency C-section.
This fetal position can prolong your labor, lead to instrumental interventions, astringent perineal tears or a C-section (3).
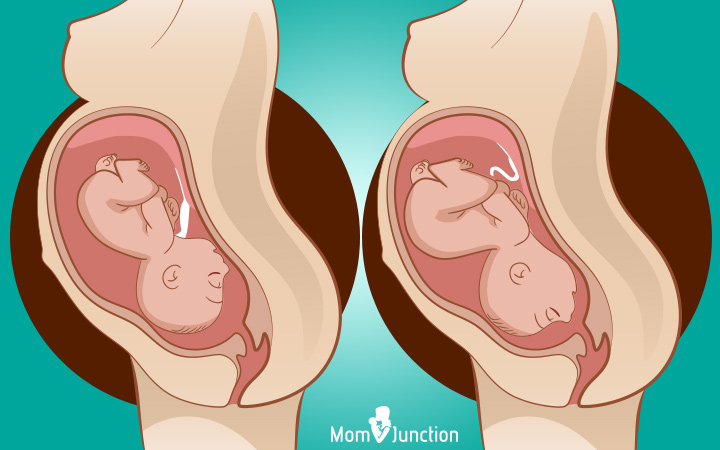
3. Occiput transverse (OT)
The baby lies sideways in the womb. If she fails to plow to the optimal position at the time of commitment, and so a C-section becomes necessary. During the vaginal exam, the medico tin can sometimes feel the shoulder, or the arm, elbow or hand prolapsing into the vagina. This position also poses the take chances of umbilical string prolapse, in which the umbilical cord comes out earlier the baby. About one% of babies in the transverse position can have a string prolapse (4), which is a medical emergency and needs an firsthand C-section.
In some cases, assisted delivery is carried out by rotating the babe manually or using forceps or vacuum to plow the baby into the platonic position.
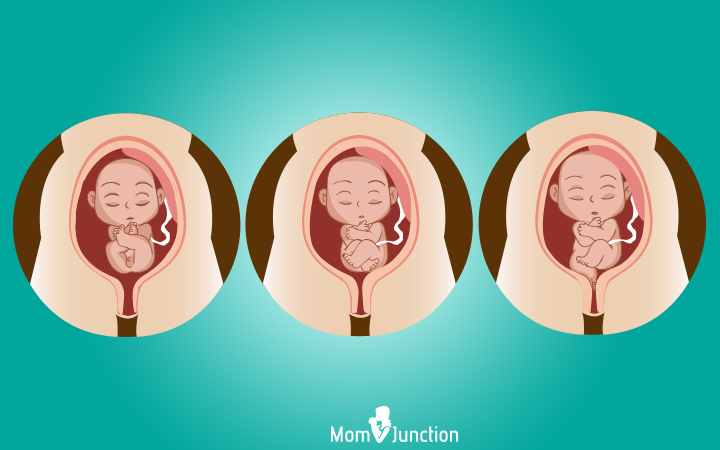
iv. Breech position
The baby is positioned with her head up and buttocks pointing towards the birthing canal. This occurs in i out of 25 total-term deliveries. There are 3 different variations of breech presentations:
i. Complete breech: The buttocks point towards the birthing canal with the legs folded at the knees and the feet positioned almost the buttocks. This position increases the risk of umbilical cord loop in a vaginal delivery. Moreover, the cord could pass through the neck before the head, causing injuries to the baby.
ii. Frank breech: The buttocks point towards the nativity canal with the legs stretching straight up and feet reaching the head. This tin can also atomic number 82 to umbilical string loop, causing injuries to the baby while attempting a vaginal nativity.
3. Footling breech: The infant'south buttocks are downwardly, with one of her feet pointing towards the birthing canal. This can cause an umbilical string prolapse that could even cut off the blood supply and oxygen to the fetus.
5. Umbilical cord presentation
During this, the umbilical cord comes out first through the birthing culvert (5). Withal, there is a difference between umbilical string presentation and prolapse based on the condition of the uterine membrane.
Whereas a string presentation happens when the umbilical cord enters the birthing canal earlier the h2o breaks, a string prolapse occurs after the water breaks, which calls for an firsthand C-department.
The positions are influenced by the health status of the female parent and the baby.
[ Read: Stages Of Childbirth ]
What Are The Risk Factors For Having A Difficult Fetal Position?
The below factors increase the take chances of fetal malpositions (6):
Maternal factors:
- In high parity women, who had more than five pregnancies of less than 20 weeks gestations (7), the abdominal wall muscle tone fails to hold the babe in a stable longitudinal lie.
- Placenta previa, where the placenta blocks the cervical opening.
- Placenta contracture occurs when the stretchy tissues are replaced by not-stretchy tissues.
- Pelvic tumors such as an ovarian cyst or a tumor in the uterus.
- Uterine malformations like uterus cordiformis, subseptus, or septus and uterus unicornis, bicornis, and didelphys can cause infinite restriction inside the uterus.
- Distended urinary float.
Fetal factors:
- Polyhydramnios – excess amniotic fluid in the birth sac — helps the fetus move freely in the womb, making information technology unstable and resulting in its malpositioning.
- Oligohydramnios – the deficiency of amniotic fluid — restricts the fetal movements.
- If the mother is carrying multiple fetuses, one or both the fetuses might change their position frequently, leading to malpositioning.
- Fetal abnormalities, such as hydrocephaly (tumors of the fetal neck or sacrum), fetal intestinal distention equally with hydrops fetalis, and fetal neuromuscular dysfunction, can prevent the fetus from engaging properly into the maternal pelvis.
These factors increase the likelihood of having an unsuitable fetal position only you lot don't accept to lose promise.
[ Read: Contractions During Pregnancy ]
Can The Fetal Position Be Corrected?
Aye. There are ii ways to correct the position of your infant. They are described beneath:
i. External cephalic version (ECV)
This medical procedure is undertaken later 37 weeks of pregnancy. The technique involves rotating the baby past applying pressure on the abdomen. The doctor places one paw over the head of the baby and the other hand on the buttocks to turn her to the optimal position.
During this procedure, the heartbeat of the baby will be closely monitored using an ultrasound. In the instance of any discrepancy in the fetal heart rate, the procedure will be stopped immediately.
This process may or may not piece of work. Studies show that about 1 in i,000 women goes into labor after an ECV while about ane in 200 women need an immediate C-department (8).
ECV is non recommended in the example of:
- Multiple pregnancies
- Unusual shape of uterus
- Recent vaginal bleeding
- Low levels of amniotic fluid
- Placenta previa
- Complicated pregnancy
two. During labor
Virtually babies turn to an platonic birthing position with the onset of labor. If it doesn't happen, if the baby doesn't engage during labor, or if the shape of the pelvis is not favorable for vaginal birthing, then a Cesarean-section is performed.
[ Read: How To Ease Imitation Labor ]
How Is Belly Mapping Done?
Belly mapping is a method for y'all to rails the position of your baby. You can exercise this from the eighth calendar month of pregnancy. However, make sure to talk to your doctor before doing information technology.
Things you crave: A marker (the ink stain should be easy to remove)
How to do:
- Lie down, depict a circle on your tummy and split information technology into four parts.
- Experience the movements of the baby. Endeavor to experience the infant'southward head by slightly putting pressure on your abdomen. The point where yous feel a ball like feature, marking information technology as the head on your belly.
- Use a fetoscope to hear your baby'due south heartbeat and mark the point. You lot will feel a long hard mass, which indicates the back of your infant. The heart is the part of this long mass.
- Next, try to find the bum, which feels like a difficult part. Marker this point on your belly.
- Now feel the kicks and wiggles equally they give you a inkling near the location of the infant's legs and knees. Mark it as well.
- Join all the points yous have marked to find the position of your baby.
Belly mapping is complicated, and you lot may or may non be able to track the baby's movements accurately. Therefore, you may gild it with a few other ways.
Other Means To Know The Position Of The Baby
Here are a few indications:
[ Read: Exercises For Normal Commitment ]
| Indications | Probable fetal position |
|---|---|
| Experience the babe'south kicks under the ribs with your navel popping out | Inductive position with head-down |
| Feel the kicks at the forepart of the tummy and the tum seems flattened | Posterior position |
| Push the lump on your bump and experience the whole baby moving | The lump is the lesser of the baby. Make up one's mind the position based on the location of that lump |
| Lump on ane side that moves past itself without any change in the positioning of the residue of the torso | The lump is the head of your baby. You tin can determine the position based on the position of the lump |
| Feel the hiccups at the bottom of the belly | Head-downwards position |
| Feel the hiccups above the belly button | Caput-upward position |
| Extreme pain nether the ribs | Caput-up position |
| Heartbeats felt in a higher place belly button | Head-up |
| Heartbeats felt below belly button | Head-down |
These are just an assumption and a way to become continued with the baby. They practice non replace your doc's communication.
[ Read: Infant Crowning ]
The fetal positioning is of import during pregnancy and labor, equally information technology decides how your labor will continue. Though the babies move into various positions, at the time of labor, they might motion into the optimal position. If they don't, so C-section is the best pick for delivery.
Do you accept annihilation to say on this? Share with the states in the comment section beneath.
Recommended Articles:
- When Is Your Baby Likely To Drop?
- Signs Of Labor And What To Practise
- Bradley Method Of Childbirth
- How To Speed Up Labor
The following ii tabs alter content below.
- Reviewer
- Author

Dr. Sangeeta Agrawal worked in Royal London, St. Bartholomew's, Northward Middlesex and Barnet Full general hospitals in London. Currently, she runs her own dispensary in Mumbai. She is as well attached to Bhatia Infirmary, Breach Candy Hospital, Wockhardt Infirmary, and Global Hospital. Her areas of expertise include obstetrics and gynecology, involving teenage care, antenatal, intrapartum, post-natal care, painless labor, fertility control, menopause... more

Shreeja holds a postgraduate degree in Chemistry and diploma in Drug Regulatory Affairs. Before joining MomJunction, she worked as a enquiry analyst with a leading multinational pharmaceutical visitor. Her interest in the field of medical research has adult her passion for writing enquiry-based articles. Equally a writer, she aims at providing informative articles on wellness and pharma, particularly related to... more
Source: https://www.momjunction.com/articles/position-baby-important-pregnancy_0078625/
0 Response to "How to Get Baby in Head Down Position"
Post a Comment